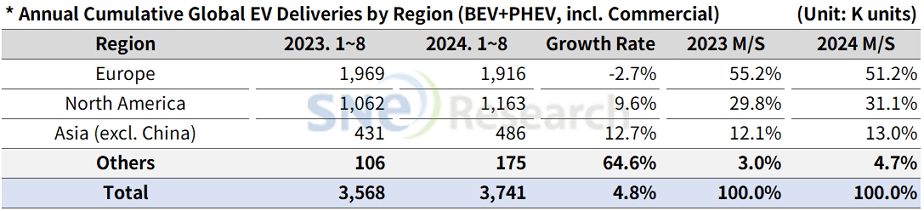
From January to August 2024, electric vehicle (EV) deliveries in countries outside China totaled approximately 3.741 million units, representing a 4.8% increase compared to the same period last year, according to SNE Research’s “Global EV & Battery Monthly Tracker – Sep 2024.”
Tesla maintained its position as the leading EV manufacturer in the non-China market, despite experiencing an 8.3% year-over-year decrease in sales. The decline was attributed to reduced sales of its primary models, the Model 3 and Model Y, which together account for about 95% of the company’s total sales. In Europe, Tesla saw a 16.2% decrease, and in North America, an 8.4% decline was recorded.
The Volkswagen Group, encompassing brands like Audi, Porsche, and Skoda, ranked second but posted a 3.6% year-over-year decline. While models such as the Audi Q4 e-tron and the ENYAQ showed steady sales growth, the Volkswagen ID series underperformed. The sluggish performance is likely due to the continued slowdown in European EV demand.
Hyundai Motor Group reported sales of approximately 362,000 units, marking a 4.1% decrease from the previous year. Although the IONIQ 5 and EV6 experienced slower sales, the global rollout of the EV9 is expanding, and deliveries of the newly launched EV3 have commenced. With significant sales drops from competitors like General Motors and Volkswagen in China, Hyundai stands to gain market share. The group anticipates a resurgence in growth with the introduction of new models like the IONIQ 9 and EV4 in Europe and North America by late 2024 or early 2025.
.jpg)
Regionally, the European market saw a 2.7% decline but still accounts for over half of the non-China EV market. Brands such as BMW (8.5% growth), Mercedes-Benz (14.7%), and Geely (21.6%) achieved notable year-over-year increases. Conversely, Tesla, Stellantis, and Renault experienced declines, indicating a challenging environment for EV growth in Europe.
North America posted a 9.3% year-over-year growth in EV deliveries. Despite Tesla’s declining sales, increased sales from Hyundai Motor Group, Stellantis, and Ford contributed to the upward trend. Notably, Hyundai Motor Group became the second-highest EV seller in North America after Tesla.
In Asia (excluding China), BYD and SAIC reported rapid sales increases of 72.7% and 74.0% year-over-year, respectively.
The European Union recently announced plans to lower tariff rates on Chinese-made electric vehicles from a maximum of 47.6% to 46.3% starting in November. Although still high, these tariffs vary based on company cooperation, with BYD facing a 27.4% rate and SAIC 46.3%. Despite regulatory challenges, Chinese EV manufacturers are expanding globally by adapting to environmental regulations and diversifying their strategies. Companies like BYD, Xpeng, Chery, and Geely are establishing local production facilities in Europe and rapidly entering South American and Southeast Asian markets. For example, BYD reported over 800% year-over-year growth in Brazil.
As the industry navigates obstacles such as reduced subsidies, insufficient infrastructure, and battery safety concerns, overcoming these challenges is critical. To effectively compete with Chinese electric vehicles, prioritizing cost competitiveness through local production and advanced battery technology is essential.
Source: SNE Research
















