In the evolving landscape of the U.S. battery manufacturing sector, several gigafactory projects are experiencing delays and cancellations, reflecting broader market uncertainties. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 initially catalyzed significant investments in domestic battery cell production, boosting planned annual capacity to over 1 terawatt-hour (TWh)—a more than 50% increase from pre-IRA levels. This legislation aimed to reshore the entire battery manufacturing supply chain, not only expanding battery cell capacity but also enhancing the production of battery materials and components within the United States.
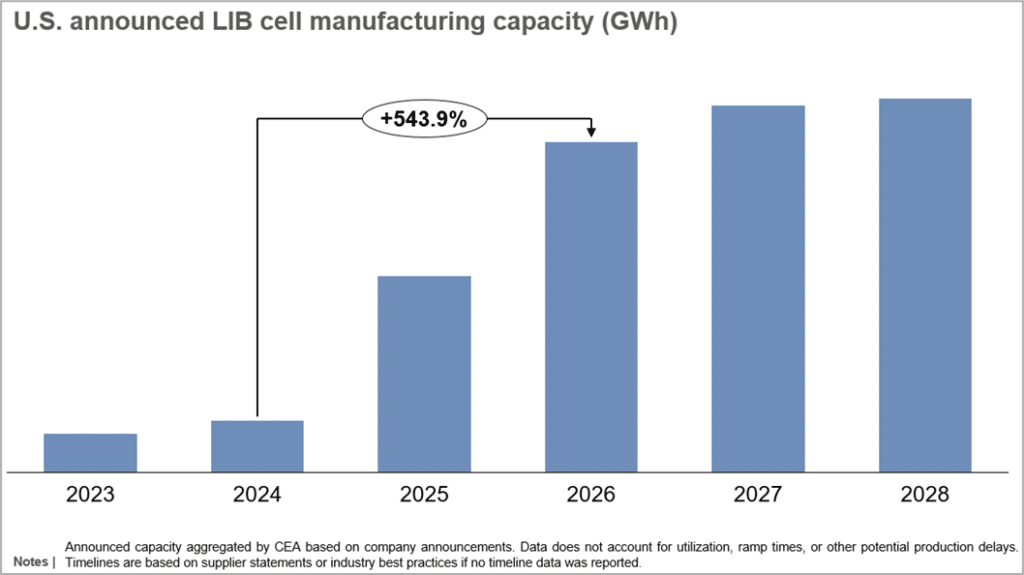
Despite these optimistic projections, recent developments have revealed challenges that threaten the momentum of these initiatives. The anticipated growth in electric vehicle (EV) demand has not met expectations, and policy reversals during the Trump administration have further complicated the landscape. Specifically, the administration’s decision to freeze funding for clean energy projects has adversely affected smaller manufacturers. Notably, two battery manufacturing projects were canceled in the first week of Trump’s presidency, and KORE Power withdrew from its planned 12 gigawatt-hour (GWh) battery cell facility in Buckeye, Arizona. The latter project’s cancellation was largely due to the delayed disbursement of an $850 million conditional loan from the Department of Energy, which was crucial for the project’s financing.
Similarly, FREYR announced the cancellation of its 34 GWh battery cell production project in Georgia earlier this year. The company shifted its focus to the Giga America project to capitalize on IRA tax credits, citing declining battery prices and rising interest rates as factors influencing its decision. Smaller suppliers across the sector are experiencing increased financial strain, leading to delayed project timelines and workforce reductions. For instance, Kontrolmatik postponed its battery cell production capacity twice in 2024 due to material sourcing challenges and rising costs. Companies like FREYR, Our Next Energy, Microvast, and iM3NY have implemented significant layoffs, with iM3NY filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy due to insufficient capital.
While these setbacks pose risks, the overall domestic battery industry remains robust, primarily due to the dominant presence of major Korean and Japanese suppliers such as LG Energy Solution, Panasonic, Samsung, and SK On. These companies account for approximately 54% of the total domestic cell production capacity projected for 2026, focusing primarily on EV applications. However, the energy storage system (ESS) segment is more vulnerable, as it represents a smaller portion of the market and is mainly served by smaller vendors facing greater challenges.
Established suppliers are positioning themselves to capitalize on the growing demand for stationary energy storage, leveraging their capital and scale to address gaps left by project cancellations and increased tariffs on Chinese imports. LG Energy Solution, for example, plans to initiate lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cell production in Holland, Michigan, while pausing construction on its ESS-dedicated facility in Arizona.
The shifting dynamics suggest that while large-scale manufacturers are well-equipped to navigate the current uncertainties, smaller vendors may find it increasingly difficult to sustain their operations in the competitive battery market.
Source: Energy Storage News
















