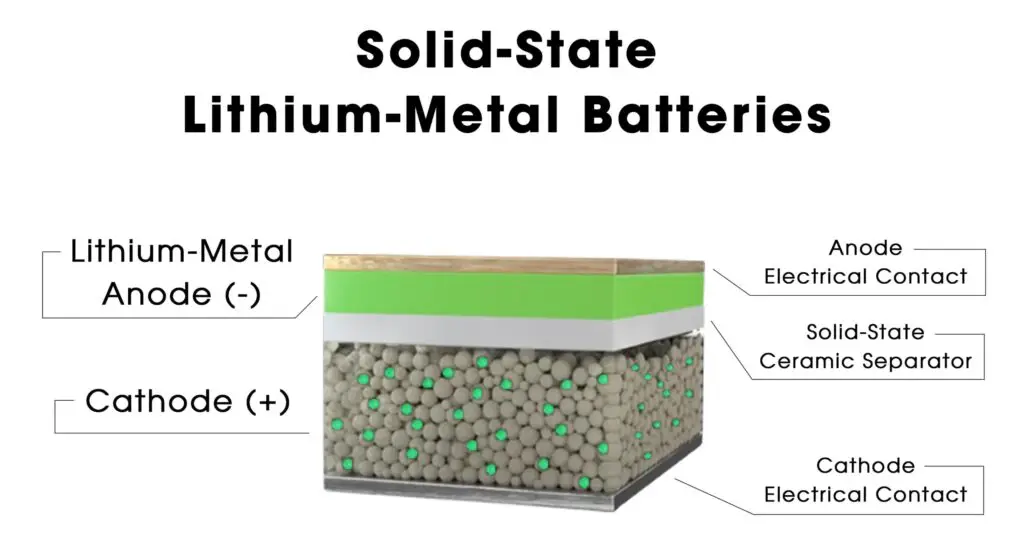
Solid-state batteries (SSBs) are an emerging technology that promises to revolutionize the energy storage industry. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid or gel electrolytes, solid-state batteries employ solid electrolytes, offering significant enhancements in safety, energy density, and charging speed.
What Are Solid-State Batteries?
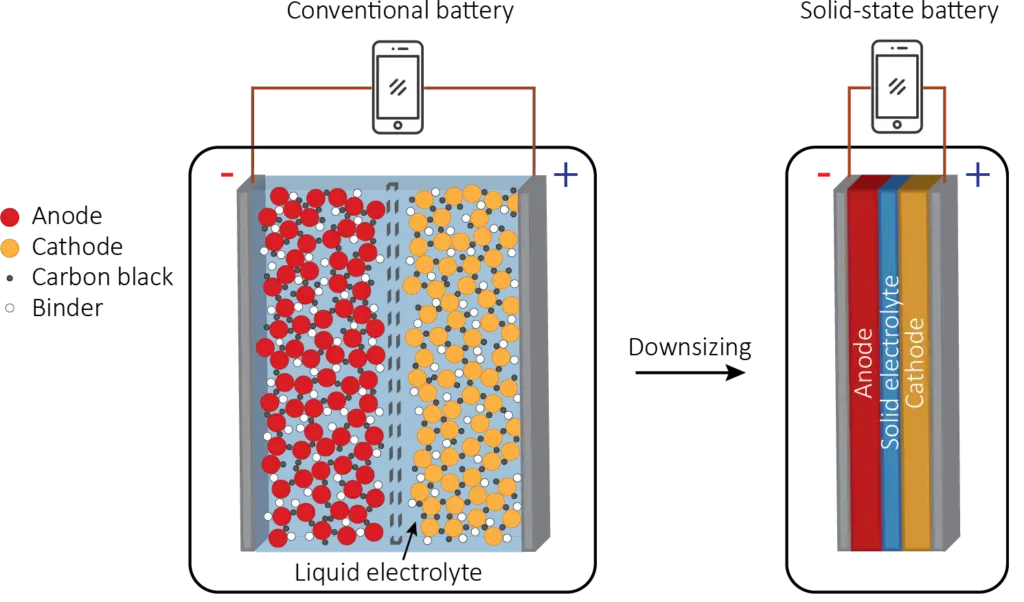
Solid-state batteries utilize a solid electrolyte made from materials such as ceramics, glass, sulfides, or solid polymers. This solid electrolyte facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging cycles. When the battery charges, lithium ions migrate from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, while electrons flow in the opposite direction. Upon discharging, this process reverses.
The absence of liquid electrolytes eliminates the risk of leaks and reduces the chances of fires or explosions, making solid-state batteries inherently safer than their lithium-ion counterparts. The solid electrolyte also contributes to a more compact and lightweight design, as it allows for thinner separators and closer electrode spacing.
Source: https://hyetlithium.com/solid-state-batteries/
Why Are Solid-State Batteries Needed?
The growing demand for safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting batteries, especially in electric vehicles (EVs), has accelerated the development of solid-state battery technology.
Advantages of SSBs
- Enhanced Safety: By replacing flammable liquid electrolytes with solid materials, solid-state batteries significantly reduce the risk of fires and explosions. This inherent safety is crucial for applications like EVs and consumer electronics.
- Higher Energy Density: Solid-state batteries can store more energy in a smaller and lighter package. This higher energy density could lead to longer driving ranges for EVs and more efficient energy storage solutions.
- Faster Charging: These batteries promise rapid charging capabilities, potentially reaching 80% charge in just 10-15 minutes, compared to the 30+ minutes typically required for traditional lithium-ion batteries. This efficiency enhances user convenience and accelerates the adoption of electric mobility.
- Extended Lifespan: Solid-state batteries are expected to endure more charge-discharge cycles with minimal degradation. Estimates suggest they can last 5,000+ cycles, potentially surpassing the lifespan of traditional lithium-ion batteries.
- Environmental Benefits: With the use of more environmentally friendly materials and a reduced carbon footprint, solid-state batteries contribute to sustainable energy practices.
Challenges in SSB commercialization
Despite their promising features, solid-state batteries face several obstacles:
- Complex Manufacturing: The production processes for solid-state batteries are more complex and costly, impeding mass production and widespread adoption.
- Performance at Low Temperatures: These batteries may exhibit reduced performance in low temperature environments compared to, for example, LFP batteries, and may require additional stabilization measures to operate efficiently at room temperature.
- Degradation Mechanisms: Issues like lithium dendrite formation, interfacial delamination, and dead lithium can lead to short circuits and diminished battery performance over time. Solid-state batteries were initially thought to be immune to dendrite growth due to the absence of liquid electrolytes. However, research has shown that dendrites can still form and propagate through solid electrolytes, leading to potential short circuits and battery failure.
Leading Companies in Solid-State Battery Development
Several companies are at the forefront of solid-state battery research and commercialization:
- QuantumScape: Focusing on solid-state batteries for electric vehicles, QuantumScape uses a lithium-metal anode and a proprietary solid ceramic separator to enhance battery performance.
- Solid Power: Developing all-solid-state rechargeable batteries using a proprietary sulfide solid electrolyte, Solid Power has partnerships with major automotive companies like BMW and Ford.
- Toyota: With an extensive patent portfolio, Toyota is a significant player in solid-state battery technology, actively researching and aiming to implement these batteries in future vehicles.
- Samsung SDI: Planning to mass-produce all-solid-state batteries by 2027, Samsung SDI is working on batteries with high energy density suitable for various applications.
- LG Energy Solution: Developing lithium-sulfur and all-solid-state batteries, LG Energy Solution aims to start mass production by 2030, contributing to advancements in EV technology.
- Find more here: Solid-State Battery: Companies List
Solid-state batteries represent a significant step forward in battery technology, offering improved safety, higher energy density, faster charging and longer life. While challenges remain in manufacturing and performance optimization, ongoing research and development by leading companies points to a promising future for solid-state batteries in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and other application areas.
Source:
- https://www.britannica.com/technology/solid-state-battery
- https://forum.cleanenergyreviews.info/t/6-advantages-of-solid-state-batteries/2754
- https://www.engineering.com/solid-state-ev-batteries-are-closer-than-you-think/
- https://www.greyb.com/blog/solid-state-battery-companies/
- https://solidpowerbattery.com/overview/default.aspx